Irritable Bowel Syndrome Treatment
A detailed clinical history is taken to eliminate the possibility of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases(e.g., Crohn's Disease, Ulcerative Colitis or Diverticulitis). It is also important to determine when the IBS symptoms started, their triggers, how they progress, their severity and frequency. At BNC, for the effective treatment of irritable bowel syndrome, we also want to gain an understanding of any psychological co-morbidities including anxiety, depression, poor sleep, fatigue, and cognitive deficits. ASD is included in this list of potential co-morbidities, since IBS can cause nutrient malabsorption, which is a maintaining factor for the behavioural issues associated with ASD.
IBS Treatment Options
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome may involve some of the following recommendations, based on clinical presentation:
- Elimination of enteric pathogens, parasites, and protozoa.
- Elimination of IgG sensitive foods.
- Elimination of foods that trigger bloating, discomfort, and loose stools, since the individual may lack enzymes to breakdown these foods e.g., lactose intolerance is due to deficits in the lactase enzyme (not to be confused with an IgG sensitivity to cow's milk).
- Recommending the healthy diet (food pyramid) proposed by Harvard Medical
- BNC’s Gut Recovery Diet may be recommended in more severe cases to starve specific overgrown bacteria.
- Promotion of oily fish consumption.
- Prescription of specific short-term antibiotics to promote an optimum gut microbiology profile.
- Recommending specific nutrient supplements to promote optimum cellular nutrition, as well as gut, immune, and brain cell repair.
- Nutritional supplementation based on the Extended Faecal Microbiology Analysis.
Contributing Factors to IBS
The red cell Essential Fatty Acid (EFA) Profile is a specialised blood test that provides detail about the fatty acid composition of red blood cells.It is a good test for identifying specific EFA deficiencies. Deficiencies in Omega 3 EFAs can be correlated with leaky gut, nutrient malabsorption, and mental health disorders.
Every cell in the body has a lipid membrane protecting its boundaries. The brain consists of 70% lipids and 40% of the brain is made up of the long chain Omega 3 EFAs (EPA and DHA, which we get from fish). Studies have consistently found that deficiencies of Omega 3 EFAs (derived from fish) are associated with serious brain and systemic dysfunctions. Many of these studies prove that Omega 3 EFAs are essential for brain function. It is known that deficits are associated with all kinds of psychiatric disorders, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, and Neurodevelopmental disorders.
Omega3 EFAs and Gut function
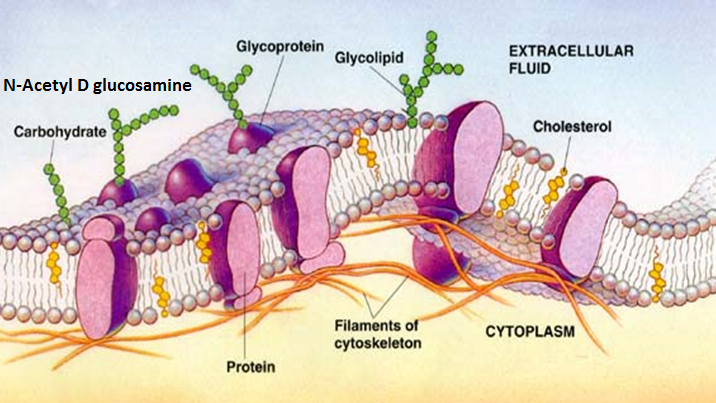
The gut cell wall (the epithelium) is exposed daily to billions of organisms and toxins. The protective role of each cell’s lipid membrane cannot be understated. If the lipid membrane is lacking in Omega 3 fatty acids, the epithelium may fail in preventingthe organisms and toxins that can irritate the gut wall. If it cannot provide adequate protection,these organisms and toxins can give rise toIrritable Bowel Syndrome and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Of course, EFA deficiencies are not the sole cause of epithelial dysfunction, there are other nutrient co-factors and systems which also need to be considered.
The Red Cell Essential Fatty Acid Profile test is used to determine whether the percentage of fatty acids in the red cells are normal or not. The results of this test help BNC clinicians determine which ratio of fish oil (EPA and DHA), and which nutrient cofactors, are appropriate for the individual.
Extended Faecal Microbiology Profile
This Bioscreen test, from a medical laboratory at Melbourne University, is used at BNC to determine the profile of gut commensals (normal community of bacteria). It is the only commercially available test in the world that accurately estimates the populations of commensal bacteria. The process involves keeping the faecal sample refrigerated in an anaerobic pouch to ensure that no oxygen reaches the sample prior to its analysis. If this does not happen, anaerobic bacteria would die upon air exposure during transportation, whilst the aerobes would continue to reproduce. Therefore, the Bioscreen method is highly accurate.
Intestinal Permeability
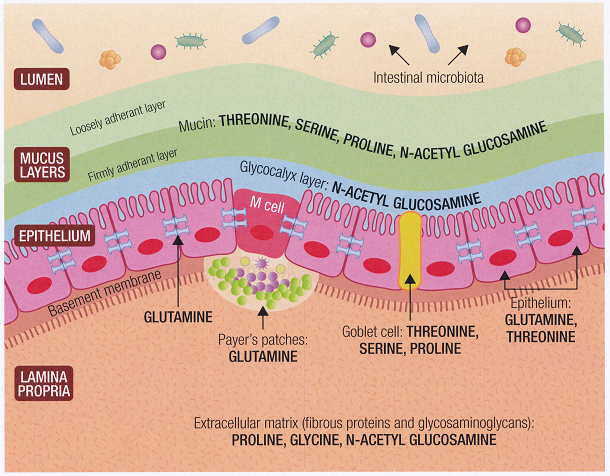
‘Leaky gut’ is a term used to imply that the gut lining has become impaired. The word ‘leaking’ is used because when the gut is in this state, molecules of partially digested food, bacteria, and/or toxins can cross the gut barrier, irritate the gut wall, or cross into the blood stream. To test for this intestinal permeability, patients are given a measured amount of two sugars (Lactulose and Manitol) and asked to collect all their urine for a period of 6 hours. The recovery of the sugars in the urine is used as a marker to estimate intestinal permeability, with higher-than-normal recovery being an indicator of ‘leaky gut’.
If ‘leaky gut’ is indicated, a nutrient compound including Glutamine, Threonine, Serine, Proline, N-Acetyl Glucosamine and Glycine may be prescribed to repair the gut wall and improve nutrient absorption.
Dietary Habits And Nutritional Uptake
Many patients with IBS have a relatively poor diet, but other eat well. Those with poor nutritional intake may encounter malabsorption issues which cause other (co-occurring) health issues. Thus, BNC offers dietary assessment and individualised nutritional supplementation for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome and to promote better overall health.
QEEG Functional Neuroimaging
QEEG neuroimaging is used to determine whether a patient’s anxiety and depression are secondary to cellular malnutrition, or primarily due to other brain-based factors such as brain asymmetry, abnormal brain power levels, or other brain patterns that are known to predispose individual to mood disturbances.




