Assessment of Post-Concussion Syndrome
In the tests described below, scores are statistically compared to large databases of people with no mental health disorders or history of head injuries. These tests have been published and validated in peer-reviewed scientific journals and are suitable for diagnostic use. They provide convergent evidence of an organic basis for post-concussion syndrome, which requires adequate nutritional supplementation and specialised Neurotherapy for tissue repair.
Methods of Assessment of Concussion
Quantitative Electroencephalography (QEEG)
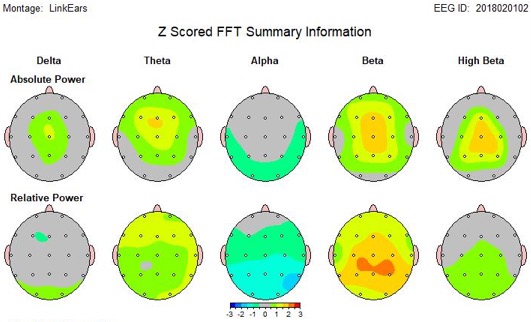
QEEG involves the statistical evaluation of the brain’s electrical activity. The QEEGs of hundreds of typically functioning people, with no mental health issues or history of head injuries, make up a normative database against which the QEEG of BNC’s patients are compared. The differences are expressed as Z scores (standardised deviations from the mean). QEEG is well-suited for the evaluation of post-concussion syndrome, since it is empirical, objective, non-intrusive and is highly accurate in identifying and discriminating the various neurophysiological patterns of brain dysfunction associated with Minor TBI and post-concussion syndrome [33-35].
A 2004 review of the scientific literature by Dr. Jacques Duff, published in the journal of the EEG and Clinical Neuroscience Society suggests that QEEG is superior to structural Neuroimaging techniques that detect brain dysfunction related to Minor TBI and post-concussion syndrome [33] which can occur with or without loss of consciousness.
Traumatic Brain Injury Discriminant Analysis
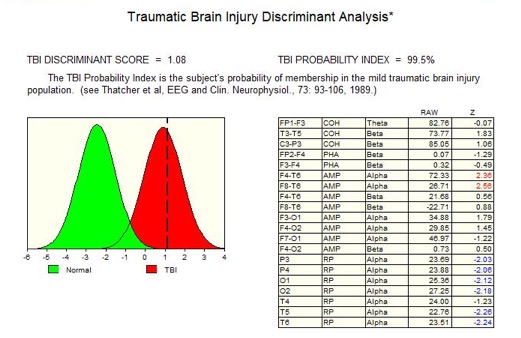
The Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) probability index provides the statistical likelihood that an individual has suffered a mild traumatic brain injury [35]. To calculate this probability, the QEEGs of hundreds of people with head injuries from Veteran Affairs Hospitals in the US were analysed, and a discriminant function was developed that reliably separated those people with head injuries from those without. The TBI probability index thus provides independent evidence that the symptoms of post-concussion syndrome have an organic basis [35].
There are over 40,000 QEEG papers published since 1990, all of which are free of false negatives in the domain of QEEG Discriminant Functions. The only critical paper about the clinical uses of QEEG was published in 1997, by Newer from the Academy of Neurology. The opinions expressed in this paper were refuted and discredited by the EEG and Clinical Neuroscience Society [36], since their findings were found to be largely unsupported. The 1997 paper lacked a comprehensive review of the current literature. After it was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) based on its clinical efficacy, the QEEG system (Neuroguide) has been used extensively in the diagnosis of Post-concussion Syndrome.
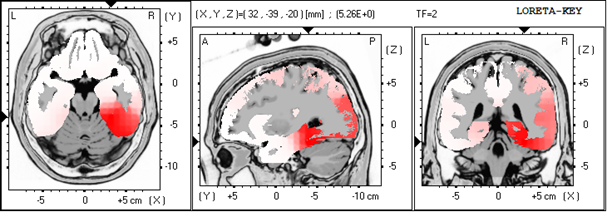
Low Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography (Loreta)
IntegNeuro Neurocognitive Test battery

IntegNeuro is used to establish the degree of cognitive impairment caused by stroke, head injury, and dementias, as well as to evaluate therapy progress. For each subtest, instructions are listened to through headphones, and the subject enters their answers into the system's touchscreen. One of IntegNeuro’s benefits is its objectivity; it is considered free of bias and human judgement since the Psychologist’s role is limited to monitoring the test.
Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA)

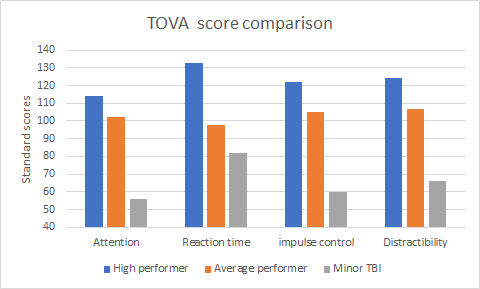
The Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA) is a highly sensitive, objective, and independent measure that quantifies impairment to the attention system, as well as measures the progress of therapy. The TOVA consists of a computer-administered continuous performance task, which requires subjects to press a specially designed micro switch whenever a ‘target’ appears on the screen. The subjects must refrain from pressing this switch when a ‘non-target’ appears. After testing, the subject’s results are compared to an age-appropriate database to produce standardised scores, which gives useful information on four variables of attention:
- Attention (the ability to concentrate and sustain mental effort)
- Impulse control (the ability to inhibit impulsiveness)
- Processing speed (reaction time)
- Distractibility (variability in reaction time)
Treatment of Post-Concussion Syndrome
A review paper in the October 2004 issue of Clinical EEG and Neuroscience concluded that QEEG is the most sensitive Neuroimaging tool for the assessment of post-concussion syndrome and that Neurotherapy is the most promising treatment [33].
1. Medication, Counselling & Cognitive Rehabilitation
Medication can provide temporary relief from pain, and counselling helps people understand the need to control their impulses and anger. However, there is no evidence that medication or cognitive rehabilitation can effectively restore the cognitive and concentration deficits associated with post-concussion syndrome.
2. Neurotherapy
People with attention deficits and MTBI tend to have an excess of slow-wave brain electrical activity and coherence abnormalities. Neurotherapy (EEG biofeedback) uses operant conditioning to give patients audio/visual rewards for producing healthier patterns of brainwave activity. Since the 1970s, studies have shown that, through Neurotherapy, patients can be taught to normalise previously dysfunctional pattern of brain activity [33, 38-41]. More recently, QEEG (rather than EEG) has been used to identify the specific brainwave patterns that need to be addressed [42-44]. Additionally, Neurotherapy can improve mood, concentration, and enhance mental performance in people with post-concussion syndrome. For a review of the literature see this peer-reviewed medical journal article: October 2004 in Clinical Electroencephalography.
References
- Thatcher, R.W., EEG operant conditioning (biofeedback) and traumatic brain injury. Clin Electroencephalography, 2000. 31(1): p. 38-44.
- Hugenholtz, H., et al., How long does it take to recover from a mild concussion? Neurosurgery, 1988. 22(5): p. 853-8.
- Slagle, D.A., Psychiatric disorders following closed head injury: an overview of biopsychosocial factors in their etiology and management. Int J Psychiatry Med, 1990. 20(1): p. 1-35.
- Fenton, G.W., The postconcussional syndrome reappraised. Clin Electroencephalogr, 1996. 27(4): p. 174-82.
- Ponsford, J. and G. Kinsella, Attentional deficits following closed-head injury. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol, 1992. 14(5): p. 822-38.
- Ponsford, J., S. Sloan, and P. Snow, Traumatic Brain Injury: Rehabilitation for everyday adaptive living. 1995, Hillsdale (USA): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Zwil, A.S., M.E. Sandel, and E. Kim, Organic and psychological sequelae of traumatic brain injury: the postconcussional syndrome in clinical practice. New Dir Ment Health Serv, 1993(57): p. 109-15.
- Stevens, M.M., Post concussion syndrome. J Neurosurg Nurs, 1982. 14(5): p. 239-44.
- Elkind, A.H., Headache and facial pain associated with head injury. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 1989. 22(6): p. 1251-71.
- Fann, J.R., et al., Psychiatric disorders and functional disability in outpatients with traumatic brain injuries. Am J Psychiatry, 1995. 152(10): p. 1493-9.
- Munoz-Cespedes, J.M., et al., [The nature, diagnosis and treatment of post-concussion syndrome]. Rev Neurol, 1998. 27(159): p. 844-53.
- Pelczar, M. and B. Politynska, [Pathogenesis and psychosocial consequences of post-concussion syndrome]. Neurol Neurochir Pol, 1997. 31(5): p. 989-98.
- Harrington, D.E., et al., Current perceptions of rehabilitation professionals towards mild traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 1993. 74(6): p. 579-86.
- Binder, L.M., Persisting symptoms after mild head injury: a review of the postconcussive syndrome. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol, 1986. 8(4): p. 323-46.
- Hilton, G., Behavioral and cognitive sequelae of head trauma. Orthop Nurs, 1994. 13(4): p. 25-32.
- Hillier, S.L., M.H. Sharpe, and J. Metzer, Outcomes 5 years post-traumatic brain injury (with further reference to neurophysical impairment and disability). Brain Inj, 1997. 11(9): p. 661-75.
- Millis, S.R., et al., Long-term neuropsychological outcome after traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil, 2001. 16(4): p. 343-55.
- Hillier, S.L. and J. Metzer, Awareness and perceptions of outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj, 1997. 11(7): p. 525-36.
- Johansson, E., M. Ronnkvist, and A.R. Fugl-Meyer, Traumatic brain injury in northern Sweden. Incidence and prevalence of long-standing impairments and disabilities. Scand J Rehabil Med, 1991. 23(4): p. 179-85.
- Malia, K., G. Powell, and S. Torode, Personality and psychosocial function after brain injury. Brain Inj, 1995. 9(7): p. 697-712.
- Max, J.E., B.A. Robertson, and A.E. Lansing, The phenomenology of personality change due to traumatic brain injury in children and adolescents. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2001. 13(2): p. 161-70.
- Gerring, J., et al., Neuroimaging variables related to development of Secondary Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder after closed head injury in children and adolescents. Brain Inj, 2000. 14(3): p. 205-18.
- Voller, B., et al., Neuropsychological, MRI and EEG findings after very mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj, 1999. 13(10): p. 821-7.
- Jansen, H.M., et al., Cobalt-55 positron emission tomography in traumatic brain injury: a pilot study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 1996. 60(2): p. 221-4.
- Rudolf, J., et al., Cerebral glucose metabolism in acute and persistent vegetative state. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol, 1999. 11(1): p. 17-24.
- Bergsneider, M., et al., Cerebral hyperglycolysis following severe traumatic brain injury in humans: a positron emission tomography study. J Neurosurg, 1997. 86(2): p. 241-51.
- Matz, P.G. and L. Pitts, Monitoring in traumatic brain injury. Clin Neurosurg, 1997. 44: p. 267-94.
- Thatcher, R.W., et al., Biophysical Linkage between MRI and EEG Amplitude in Closed Head Injury. Neuroimage, 1998. 7(4): p. 352-367.
- Thatcher, R.W., et al., Biophysical linkage between MRI and EEG coherence in closed head injury. Neuroimage, 1998. 8(4): p. 307-26.
- Thatcher, R.W., et al., Quantitative MRI of the gray-white matter distribution in traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma, 1997. 14(1): p. 1-14.
- Shaw, N.A., The neurophysiology of concussion. Prog Neurobiol, 2002. 67(4): p. 281-344.
- Montgomery, E.A., et al., The psychobiology of minor head injury. Psychol Med, 1991. 21(2): p. 375-84.
- Duff, J., The usefulness of Quantitative EEG (QEEG) and Neurotherapy in the Assessment, and Treatment of Post-Concussion Syndrome. Clinical EEG and Neuroscience, 2004. 35(4): p. 1-12.
- Hughes, J.R. and E.R. John, Conventional and quantitative electroencephalography in psychiatry. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 1999. 11(2): p. 190-208.
- Thatcher, R.W., et al., EEG discriminant analyses of mild head trauma. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol, 1989. 73(2): p. 94-106.
- Thatcher, R.W., et al., QEEG and traumatic brain injury: rebuttal of the American Academy of Neurology 1997 report by the EEG and Clinical Neuroscience Society. Clin Electroencephalogr, 1999. 30(3): p. 94-8.
- Gordon, E., Integrative neuroscience in psychiatry: the role of a standardized database. Australasian Psychiatry, 2003. 11(2): p. 156-163.
- Lubar, J.F., Discourse on the development of EEG diagnostics and biofeedback for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders. Biofeedback and Self Regulation, 1991. 16(3): p. 201-225.
- Sterman, M.B., Sensorimotor EEG operant conditioning: Experimental and clinical effects. Pavlovian Journal of Biological Science, 1977. 12(2): p. 63-92.
- Sterman, M.B., EEG biofeedback: physiological behavior modification. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 1981. 5(3): p. 405-12.
- Thompson, L. and M. Thompson, Neurofeedback combined with training in metacognitive strategies: Effectiveness in students with ADD. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 1998. 23(4): p. 243-263.
- Thatcher, R.W., Normative EEG databases and EEG biofeedback. Journal of Neurotherapy, 1998. 2(4): p. 8-39.
- Thatcher, R.W., EEG database guided neurotherapy, in Introduction to Quantitative EEG and Neurofeedback, A. Abarbanel, Editor. 1999, Academic Press: San Diego.
- Sterman, M.B., Physiological origins and functional correlates of EEG rhythmic activities: Implications for self-regulation. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 1996. 21(1): p. 3-33.
